Based on location and function, the right connectivity solution must be evaluated and selected for the various scenarios:
- Smart devices (endpoints)
- Device-to-cloud connections
- Connectivity within the cloud
- User connectivity (cloud-to-user)
Data Distribution Service Standard
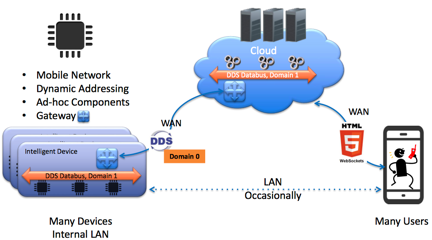
Between the devices and the cloud (WAN connections), DDS provides an ideal solution with:
- Stateful interactions
- Intelligent connections/disconnects, and the ability to resend only relevant data upon reconnection
- Intelligence built into the bus, without application overhead
- Many data-flow patterns, for meeting current and future requirements
- Publish-subscribe architecture style that is data-driven
- Scalability, performance, resilience, and security
Inside the endpoint devices themselves, DDS has been applied broadly for the same reasons listed above for device- to-cloud connections. Additionally, DDS makes it possible to design smart devices that operate very reliably and meet safety and longevity requirements in industries such as healthcare and automotive. DDS also supports diversity of transports and platforms within a system, as previously discussed in terms of gateway capabilities and routing services.
DDS has also made inroads in the cloud. Here, the requirements span a broader range and give rise to a mixture of connectivity options. DDS can support this connectivity diversity, and it can also promote longevity of cloud solutions.
In contrast, other technologies make more sense for the user-to-cloud WAN connections (see illustration). At this point in the connectivity model, traditional web technologies such as web sockets and HTTP meet the human-centric requirements with:
- Stateless interactions
- Single data-flow pattern (query)
- Request-response architecture style that is human-driven
- Established scalability and security infrastructure
- Forgiving performance and resilience (including easy-to-restart connections and applications)
- Ubiquitous access from mobile devices or thin clients
Deployment Flexibility
DDS domains make it easy to isolate subsystems with individual data communication planes. Besides facilitating security rules with logical separation, domains also make it possible to tailor endpoint discovery rules and activity levels and significantly reduce network bandwidth and CPU/memory overhead over gateway connections. As shown in the previous diagram, for example, DDS domains can be defined with:
- Domain 0 on the WAN connections. Within Domain 0, discovery can be limited to detection of the gateway endpoints and routing services. (These gateways act as proxies for the endpoint devices in their realms.)
- Domain 1 encompassing the devices and the cloud. Full device discovery can be carried out on the device and cloud buses.
DDS also supports a choice of transports, including UDP, TCP, shared memory, OpenSSL (TLS/SSL, DTLS), and low-bandwidth connections. For example, in the generic use case, the DDS connectivity between devices and the cloud can utilize DDS over TCP. Typically, transport guidelines are different for:
- LANs: Use UDP (with multicast, if available). This applies within a cloud or for application-to-application communications.
- WANs: For device-to-cloud communications, use TCP (with TLS).
DDS is being adopted for this last category to provide remote access to any DDS data bus. DDS can manage state for seamless data-sharing and switching between cellular and Wi-Fi networks. State is managed independently of the network mobility and switching, and DDS Quality of Service (QoS) can introduce resilient rules for distributing and managing state information.
Finally, for cloud-to-human communications (mobile user endpoint devices or thin clients), you can use traditional web sockets and HTTP(s) (over TCP).
For an online demonstration of remote access from web applications, visit the RTI Connext DDS Demo site at http://info.rti.com/demo_iot.
Posts by Tag
- Developers/Engineer (306)
- Connext DDS Suite (186)
- IIoT (125)
- News & Events (124)
- Standards & Consortia (122)
- Technology (74)
- Leadership (73)
- 2020 (54)
- Aerospace & Defense (50)
- Automotive (50)
- 2023 (35)
- Cybersecurity (34)
- Healthcare (33)
- Culture & Careers (31)
- 2022 (29)
- Connext DDS Tools (21)
- 2021 (19)
- Connext DDS Pro (19)
- 2024 (18)
- Energy Systems (16)
- Military Avionics (15)
- FACE (13)
- Connext DDS Micro (12)
- Connectivity Technology (10)
- JADC2 (10)
- ROS 2 (10)
- Transportation (9)
- Connext DDS Cert (7)
- Databus (7)
- Oil & Gas (5)
- Case + Code (4)
- Connext Conference (4)
- Connext DDS (4)
- FACE Technical Standard (4)
- RTI Labs (4)
- Research (3)
- Robotics (3)
- #A&D (2)
- Edge Computing (2)
- MDO (2)
- MS&T (2)
- TSN (2)
- ABMS (1)
- C4ISR (1)
- ISO 26262 (1)
- L3Harris (1)
- LabView (1)
- MathWorks (1)
- National Instruments (1)
- Simulation (1)
- Tech Talks (1)
- UAM (1)
- Videos (1)
- eVTOL (1)
 Success-Plan Services
Success-Plan Services RTI
RTI