3 min read
Deploy DDS Applications on Kubernetes: A Step-By-Step Guide | RTI
 Kyoungho An
:
May 28, 2020
Kyoungho An
:
May 28, 2020

Scalable Software Delivery for Your DDS Systems - Part 2 of 2
Last week in Part 1, I provided an overview of Kubernetes (k8s) and explained how it can improve software delivery in large-scale DDS systems. Today in Part 2, I would like to go through detailed instructions on how to deploy Data Distribution Service™ (DDS) applications on k8s for you to use as reference. Let’s get started!
Checklist to Deploy DDS Applications on Kubernetes
To deploy DDS applications on k8s, you’ll first need to complete the following steps:
- Develop a build file for a Docker image.
- Build a Docker image and push it to a Docker repository.
- Develop k8s manifest files.
- Deploy containers with the k8s manifest files.
I will now walk you through each of these steps using RTI Perftest as an example DDS application (see Figure 1). We’ll assume you already have your own k8s cluster and kubectl (that can access the cluster) installed on your machine. k8s integrates multiple virtual networking solutions such as Calico, Flannel and WeaveNet as plugins and you only need to pick one of them. I picked WeaveNet because it supports multicast and therefore I did not need to configure anything for DDS discovery.
If you use other networking solutions that do not support multicast, such as Calico and Flannel, you should run Cloud Discovery Service (CDS). CDS is our experimental product that handles discovery over networks that do not offer support for multicast capabilities.
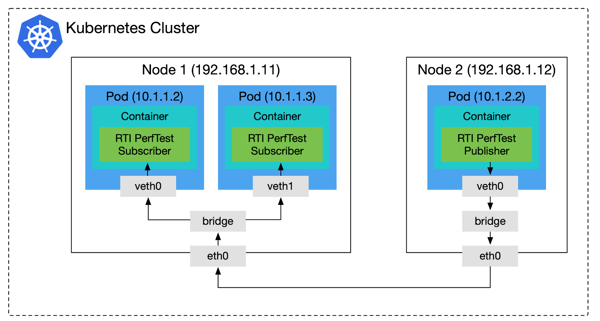
Figure 1. Kubernetes Networking Under the Hood
Step 1. Develop a build file for Docker image
| FROM ubuntu:18.04 as builder |
Dockerfile for RTI Perftest
Step 2. Build a Docker image and push it to a Docker repository
Run the following command to build a Docker image for RTI Perftest.
$ docker build -t DOCKER_REGISTRY_URL/rti-perftest:v3.0.1 .
After that, you can push the build image to a Docker repository.
$ docker push DOCKER_REGISTRY_URL/rti-perftest:v3.0.1
The pushed Docker image should be accessible by your k8s worker nodes.
Step 3. Develop k8s manifest files
Next, Kubernetes manifest files for RTI Perftest publisher and subscriber need to be developed.
| --- apiVersion: "apps/v1" kind: "Deployment" metadata: name: "rtiperftest-pub" namespace: "default" labels: app: "rtiperftest-pub" spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: "rtiperftest-pub" template: metadata: labels: app: "rtiperftest-pub" spec: containers: - name: "rtiperftest-pub" image: "kyoungho/rti-perftest:v3.0.1" env: - name: "perftest_args" value: "-pub" |
Kubernetes Manifest for RTI Perftest Publisher (rtiperftest_pub.yaml)
| --- apiVersion: "apps/v1" kind: "Deployment" metadata: name: "rtiperftest-sub" namespace: "default" labels: app: "rtiperftest-sub" spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: "rtiperftest-sub" template: metadata: labels: app: "rtiperftest-sub" spec: containers: - name: "rtiperftest-sub" image: "kyoungho/rti-perftest:v3.0.1" env: - name: "perftest_args" value: "-sub" |
Kubernetes Manifest for RTI Perftest Subscriber (rtiperftest_sub.yaml)
Step 4. Deploy containers with the manifest files and scale them up
The last step is to deploy containers with the manifest files via kubectl.
$ kubectl apply -f rtiperftest_pub.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f rtiperftest_sub.yaml
After running the commands, you can check if they are successfully deployed and running.
$ kubectl get pods
You should see something like this:
| NAME | READY | STATUS | RESTARTS | AGE |
| rtiperftest-pub-6b56f4cc86-ds88h | 1/1 | Running | 0 | 32s |
| rtiperftest-sub-8549bc57bf-n7wnf | 1/1 | Running | 0 | 10s |
Once the pods are running, you can get the logs of a specific pod.
$ kubectl logs rtiperftest-sub-8549bc57bf-n7wnf
RTI Perftest 3.0.1 (RTI Connext DDS 6.0.0)
You can simply scale up the subscriber by running the following command.
$ kubectl scale -replica=3 deployment/rtiperftest-sub
Conclusion
k8s can simplify remote deployment and scaling of applications with declarative manifests. I did not demonstrate it here, but k8s can self-heal by automatically spinning up pods on healthy nodes when they fail and can also remotely perform rolling updates and rollbacks.
DDS works pretty well for pod-to-pod communications inside a k8s cluster. If you use a networking plugin supporting multicast, DDS can automatically handle discovery for your applications without relying on a stable IP address and DNS name provided by a k8s Service.
However, there are still some questions you may have when deploying DDS applications on Kubernetes, such as:
- How can we expose DDS communications outside of a k8s cluster?
- How can we replicate stateful DDS services?
- What is the performance overhead over k8s virtual networks?
If you want to expose DDS communications outside of a cluster and replicate stateful DDS services, please check out the following example configurations:
- External Communications with RTI Routing Service with Real-time WAN Transport
- Replicating Routing Services with Real-time WAN Transport
We conducted performance evaluations of Connext with multiple k8s virtual networking solutions including Flannel, Weave, and kube-router. You can find the performance results in this paper.
We will share additional use cases and example configurations related to Kubernetes through this GitHub repository in the future. Please check it out!
See also:
Part 1: Kubernetes Explained: How It Can Improve Software Delivery in Large-Scale DDS Systems
About the author
 Kyoungho An is a Senior Research Engineer at Real-Time Innovations (RTI). He has 10 years of experience with distributed real-time embedded systems. His research interest includes publish/subscribe middleware, and deployment and monitoring of distributed systems. He has been leading several DOD and DOE funded research projects as a principal investigator. He has published research papers in journals and conferences focusing on distributed event-based systems, middleware, and cyber-physical systems. He holds a Ph.D. in Computer Science from Vanderbilt University.
Kyoungho An is a Senior Research Engineer at Real-Time Innovations (RTI). He has 10 years of experience with distributed real-time embedded systems. His research interest includes publish/subscribe middleware, and deployment and monitoring of distributed systems. He has been leading several DOD and DOE funded research projects as a principal investigator. He has published research papers in journals and conferences focusing on distributed event-based systems, middleware, and cyber-physical systems. He holds a Ph.D. in Computer Science from Vanderbilt University.
Posts by Tag
- Developers/Engineer (181)
- Technology (80)
- Connext Suite (77)
- News & Events (75)
- Aerospace & Defense (55)
- 2020 (54)
- Standards & Consortia (51)
- Automotive (38)
- 2023 (34)
- 2022 (29)
- IIoT (27)
- 2025 (25)
- Leadership (24)
- Healthcare (23)
- 2024 (22)
- Connectivity Technology (22)
- Cybersecurity (20)
- 2021 (18)
- Culture & Careers (15)
- Military Avionics (15)
- FACE (13)
- Connext Pro (10)
- JADC2 (10)
- ROS 2 (10)
- Connext Tools (7)
- Connext Micro (6)
- Databus (6)
- 2026 (5)
- AI (5)
- Transportation (5)
- Case + Code (4)
- Connext (4)
- Connext Cert (4)
- Energy Systems (4)
- FACE Technical Standard (4)
- Golden Dome (3)
- Oil & Gas (3)
- RTI Labs (3)
- Research (3)
- Robotics (3)
- Connext Conference (2)
- Data Streaming (2)
- Edge Computing (2)
- MDO (2)
- MS&T (2)
- TSN (2)
- ABMS (1)
- C4ISR (1)
- DOD (1)
- ISO 26262 (1)
- L3Harris (1)
- LabView (1)
- MOSA (1)
- MathWorks (1)
- National Instruments (1)
- Simulation (1)
- Tech Talks (1)
- UAM (1)
- Videos (1)
- eVTOL (1)
 Success-Plan Services
Success-Plan Services